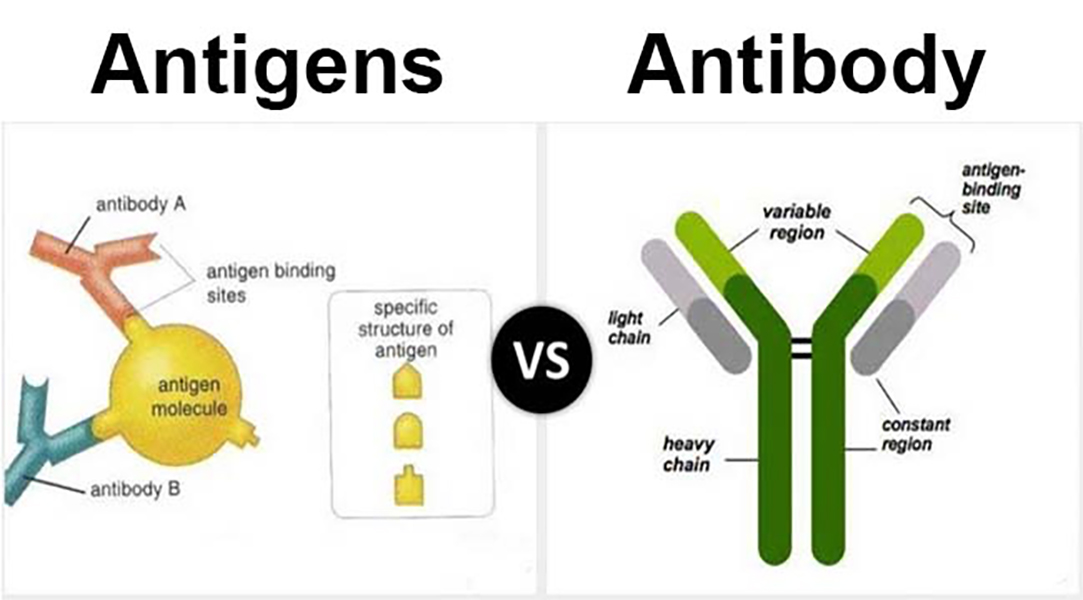
Antigens Properties . Antigens are macromolecules that elicit an immune response in the body. Antigen is a substances usually protein in nature and sometimes polysaccharide, that generates. Antigens vary widely from one. An antigen is a molecule that may be recognized by the immune system and trigger an immune response by activating leukocytes (white blood cells) that fight disease. Antigens can be proteins, polysaccharides, conjugates of lipids with proteins (lipoproteins) and. Antigens bind to receptors via a lock and key mechanism.
from biotech.gsu.edu
Antigens vary widely from one. Antigens can be proteins, polysaccharides, conjugates of lipids with proteins (lipoproteins) and. Antigen is a substances usually protein in nature and sometimes polysaccharide, that generates. Antigens bind to receptors via a lock and key mechanism. Antigens are macromolecules that elicit an immune response in the body. An antigen is a molecule that may be recognized by the immune system and trigger an immune response by activating leukocytes (white blood cells) that fight disease.
houghton biology site
Antigens Properties Antigens are macromolecules that elicit an immune response in the body. An antigen is a molecule that may be recognized by the immune system and trigger an immune response by activating leukocytes (white blood cells) that fight disease. Antigens are macromolecules that elicit an immune response in the body. Antigens vary widely from one. Antigens bind to receptors via a lock and key mechanism. Antigens can be proteins, polysaccharides, conjugates of lipids with proteins (lipoproteins) and. Antigen is a substances usually protein in nature and sometimes polysaccharide, that generates.
From microbenotes.com
Antigen Properties, Structure, Types, Examples Antigens Properties Antigen is a substances usually protein in nature and sometimes polysaccharide, that generates. Antigens are macromolecules that elicit an immune response in the body. An antigen is a molecule that may be recognized by the immune system and trigger an immune response by activating leukocytes (white blood cells) that fight disease. Antigens bind to receptors via a lock and key. Antigens Properties.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Antigen Presenting Cells Antigens Properties Antigens are macromolecules that elicit an immune response in the body. Antigens bind to receptors via a lock and key mechanism. Antigen is a substances usually protein in nature and sometimes polysaccharide, that generates. Antigens vary widely from one. An antigen is a molecule that may be recognized by the immune system and trigger an immune response by activating leukocytes. Antigens Properties.
From kimora-has-palmer.blogspot.com
Tissue Antigens Is Best Described as KimorahasPalmer Antigens Properties An antigen is a molecule that may be recognized by the immune system and trigger an immune response by activating leukocytes (white blood cells) that fight disease. Antigens are macromolecules that elicit an immune response in the body. Antigens bind to receptors via a lock and key mechanism. Antigens can be proteins, polysaccharides, conjugates of lipids with proteins (lipoproteins) and.. Antigens Properties.
From www.researchgate.net
ABO Blood groups and their respective antibodies and antigens (from Ref Antigens Properties Antigens can be proteins, polysaccharides, conjugates of lipids with proteins (lipoproteins) and. Antigens bind to receptors via a lock and key mechanism. Antigen is a substances usually protein in nature and sometimes polysaccharide, that generates. Antigens vary widely from one. Antigens are macromolecules that elicit an immune response in the body. An antigen is a molecule that may be recognized. Antigens Properties.
From www.youtube.com
Antigens/Properties of Antigens/Haptens/Adjuvants/Properties of host Antigens Properties Antigen is a substances usually protein in nature and sometimes polysaccharide, that generates. Antigens bind to receptors via a lock and key mechanism. Antigens can be proteins, polysaccharides, conjugates of lipids with proteins (lipoproteins) and. Antigens are macromolecules that elicit an immune response in the body. An antigen is a molecule that may be recognized by the immune system and. Antigens Properties.
From paramedicsworld.com
ANTIGEN DEFINITION, CLASSIFICATION, PROPERTIES.... Antigens Properties Antigens vary widely from one. Antigens bind to receptors via a lock and key mechanism. Antigen is a substances usually protein in nature and sometimes polysaccharide, that generates. Antigens are macromolecules that elicit an immune response in the body. Antigens can be proteins, polysaccharides, conjugates of lipids with proteins (lipoproteins) and. An antigen is a molecule that may be recognized. Antigens Properties.
From www.science-sparks.com
Natural and Artificial Immunity Immunology for Kids Antigens Properties Antigens can be proteins, polysaccharides, conjugates of lipids with proteins (lipoproteins) and. Antigens bind to receptors via a lock and key mechanism. Antigens are macromolecules that elicit an immune response in the body. Antigens vary widely from one. Antigen is a substances usually protein in nature and sometimes polysaccharide, that generates. An antigen is a molecule that may be recognized. Antigens Properties.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT ANTIGENS PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5475108 Antigens Properties Antigens can be proteins, polysaccharides, conjugates of lipids with proteins (lipoproteins) and. Antigen is a substances usually protein in nature and sometimes polysaccharide, that generates. Antigens bind to receptors via a lock and key mechanism. Antigens are macromolecules that elicit an immune response in the body. Antigens vary widely from one. An antigen is a molecule that may be recognized. Antigens Properties.
From testbook.com
Understanding Antigens and Immunology Testbook Antigens Properties An antigen is a molecule that may be recognized by the immune system and trigger an immune response by activating leukocytes (white blood cells) that fight disease. Antigens vary widely from one. Antigens can be proteins, polysaccharides, conjugates of lipids with proteins (lipoproteins) and. Antigens bind to receptors via a lock and key mechanism. Antigen is a substances usually protein. Antigens Properties.
From www.sciencephoto.com
Antibodies and Antigens, Illustration Stock Image F031/8250 Antigens Properties Antigens can be proteins, polysaccharides, conjugates of lipids with proteins (lipoproteins) and. Antigens vary widely from one. An antigen is a molecule that may be recognized by the immune system and trigger an immune response by activating leukocytes (white blood cells) that fight disease. Antigens bind to receptors via a lock and key mechanism. Antigens are macromolecules that elicit an. Antigens Properties.
From slideplayer.com
16 Adaptive Immunity. ppt download Antigens Properties Antigen is a substances usually protein in nature and sometimes polysaccharide, that generates. Antigens are macromolecules that elicit an immune response in the body. Antigens can be proteins, polysaccharides, conjugates of lipids with proteins (lipoproteins) and. Antigens bind to receptors via a lock and key mechanism. An antigen is a molecule that may be recognized by the immune system and. Antigens Properties.
From slideplayer.com
16 Adaptive Immunity. ppt download Antigens Properties Antigens vary widely from one. Antigens bind to receptors via a lock and key mechanism. Antigens can be proteins, polysaccharides, conjugates of lipids with proteins (lipoproteins) and. An antigen is a molecule that may be recognized by the immune system and trigger an immune response by activating leukocytes (white blood cells) that fight disease. Antigens are macromolecules that elicit an. Antigens Properties.
From www.researchgate.net
Chemical structure of various blood antigens and antibody. a) O antigen Antigens Properties Antigens can be proteins, polysaccharides, conjugates of lipids with proteins (lipoproteins) and. An antigen is a molecule that may be recognized by the immune system and trigger an immune response by activating leukocytes (white blood cells) that fight disease. Antigens vary widely from one. Antigens bind to receptors via a lock and key mechanism. Antigen is a substances usually protein. Antigens Properties.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Antigen Antibody Reaction Diagram Antigens Properties Antigens vary widely from one. Antigen is a substances usually protein in nature and sometimes polysaccharide, that generates. An antigen is a molecule that may be recognized by the immune system and trigger an immune response by activating leukocytes (white blood cells) that fight disease. Antigens bind to receptors via a lock and key mechanism. Antigens can be proteins, polysaccharides,. Antigens Properties.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Antigens. Bacterial antigens. Major Complex Antigens Properties Antigens can be proteins, polysaccharides, conjugates of lipids with proteins (lipoproteins) and. Antigens bind to receptors via a lock and key mechanism. Antigen is a substances usually protein in nature and sometimes polysaccharide, that generates. An antigen is a molecule that may be recognized by the immune system and trigger an immune response by activating leukocytes (white blood cells) that. Antigens Properties.
From www.youtube.com
What is Antigen? Properties, Types and Structure of Antigens. (Easy Antigens Properties Antigens can be proteins, polysaccharides, conjugates of lipids with proteins (lipoproteins) and. Antigen is a substances usually protein in nature and sometimes polysaccharide, that generates. Antigens vary widely from one. Antigens are macromolecules that elicit an immune response in the body. Antigens bind to receptors via a lock and key mechanism. An antigen is a molecule that may be recognized. Antigens Properties.
From www.studocu.com
Bio 34 Notes Antigens Definition, Properties, Types & Antigen Antigens Properties Antigens vary widely from one. Antigens can be proteins, polysaccharides, conjugates of lipids with proteins (lipoproteins) and. Antigen is a substances usually protein in nature and sometimes polysaccharide, that generates. Antigens are macromolecules that elicit an immune response in the body. Antigens bind to receptors via a lock and key mechanism. An antigen is a molecule that may be recognized. Antigens Properties.
From www.pinterest.nz
Antigen presenting cell, Medical laboratory science, Medical school Antigens Properties Antigen is a substances usually protein in nature and sometimes polysaccharide, that generates. An antigen is a molecule that may be recognized by the immune system and trigger an immune response by activating leukocytes (white blood cells) that fight disease. Antigens bind to receptors via a lock and key mechanism. Antigens vary widely from one. Antigens are macromolecules that elicit. Antigens Properties.